Know Your Heartbeats: Beware of That Short-Circuit In Your Heart!

Everyone in today’s world is quite aware of the oft spoken or discussed “heart attacks”. However, today, millions of people around the world are suffering from various forms of electrical or heart rhythm disorders, which remains potentially undiagnosed or untreated. These diseases have secured the No. 2 killer status globally, second only to cancer-related deaths.
The common heart attacks result from the clogging the heart arteries, which can be managed by opening them up by angiography and stenting by the interventional cardiologists. In contrary, electrical heart diseases result from abnormalities or short-circuiting in the electrical system of the heart and shouldn’t be confused with heart attacks.
Cardiac Electrophysiology is the most complex and advanced branch of Cardiology and it deals with these electrical abnormalities of the heart. Highly trained specialists (cardiac rhythm specialists or the cardiac electrophysiologists) specialize in managing these electrical ailments of the heart.
The common complaint of the patient with rhythm disorder may be palpitation, fluttering sensation or extreme racing of the heart. At times it may be benign, but often it can be life threatening.
Spectrums of heart rhythm disorders:
Rapid & slow heart beats:
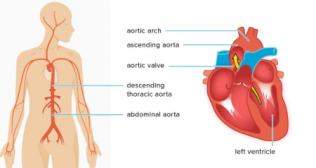
Each heart has its own normal rhythm brought about by the seamless flow of electrical impulses that begins in the heart’s natural “pacemaker” or the sinus node.
An abnormally fast heart rhythm, or tachycardia, can result from very fast electrical activities or short-circuiting in the electrical circuit of the heart. It can be dangerous as it can interfere with the heart’s ability to pump blood properly. Similarly, extreme slowing of one’s pulse or heart blocks can be due to poor electrical flow through this wiring system of the heart and the natural pacemakers. These can be life-threatening as well. Normally during sleep, the heart rate slows down significantly and it can be a normal phenomenon. But an abnormally slow heartbeat is the result of dysfunction of the natural pacemakers or the electrical wiring system of the heart.
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is another most common heart rhythm disorder today, contributing to significant morbity and healthcare expenditure worldwide. It can lead to palpitations, fatigue, and even heart failure in the long run. The most devastating effect of this disorder is a significantly increased risk of stroke and heart failure. A chance of having a stroke increases five folds for those with AF than for those without AF. Hence, it is important to know your risk of having a stroke and consult your heart rhythm specialist for an appropriate treatment strategy.
The symptoms of these heart rhythm disorders can be occasional skipped beats, palpitations, shortness of breath, chest pain, dizziness, lightheadedness, fatigue, blackouts, fainting or near fainting, chaotic, quivering, or irregular rhythm.
Sudden cardiac arrests or deaths (SCD/SCA) are the most devastating outcome of an extremely abnormal, chaotic and fast electrical impulses arising from ventricles or the bottom chambers of the heart. An old heart attack individual with family history of sudden deaths, certain genetic abnormalities, and even a susceptible individual with a visibly normal heart can meet such a devastating end.
Who is at risk of developing heart rhythm problems?
The heart rhythm disorders - both slow and the fast heartbeats - can affect persons with both normal heart or with prior heart diseases. It can be serious or life-threatening in individuals with prior heart attack, cardiac surgery, with certain inherited genetic electrical heart defects, or with advancing age.
The cardiac rhythm specialist can perform EP studies and ablations for treatment of these abnormally fast heart rhythm ailments in a specially designed EP Lab outfitted with advanced technology and equipment. During the EP study, the specialist can precisely locate the areas of electrical short-circuiting and deliver various forms of energy through catheters to make the small area(s) causing the problem to be inactive. This puts an end to arrhythmias that originated at the problematic site.
EP studies are most often recommended for patients with symptoms suggesting heart rhythm disorders or for people who may be at risk for Sudden Cardiac Death (cardiac arrest).
Persons with inherited heart diseases and patients with recurrent fainting attacks should also be evaluated at the inherited heart disease clinic by a specialist.
Dr. Rajat Sharma,
Cardiac Electrophyioslogist
Fortis Hospital Mohali
Categories
Clear allMeet the doctor

- Cardiac Sciences | Electrophysiology
-
15 Years
-
1750